It has been quite a long time since I have developed a Website. The last one I made was probably the Website that I designed and developed for my brother (http://www.simusic.hk/) many years ago. At that time, the Website was developed using PHP, JQuery and Bootstrap. Since then, I have been mainly working in the areas of machine learning, data mining and natural language processing, and have left frontend development behind.
Frontend technologies, like many other areas in software development, have changed a lot in the past years. I know about Angular, React and Vue.js, but have never really gone back to learn the basics until now. Recently, I would like to explore the idea of quickly building a Website that shows dynamic content stored in a database. After some exploration, I found that the following combination seems a quick and convenient way to achieve something similar:
- Use Vue.js to build the frontend Web app
- Use Google Sheets to store the data
- Publish the Google Spreadsheet online, and retrieve the data in JSON format in the Web app
This post describes how the above idea is used to implement a Web app that displays quotations stored in a Google Spreadsheet. The source code can be found on the github repository, and the Webapp can be found published here https://albertauyeung.github.io/quotes-app/. A screenshot is shown below:
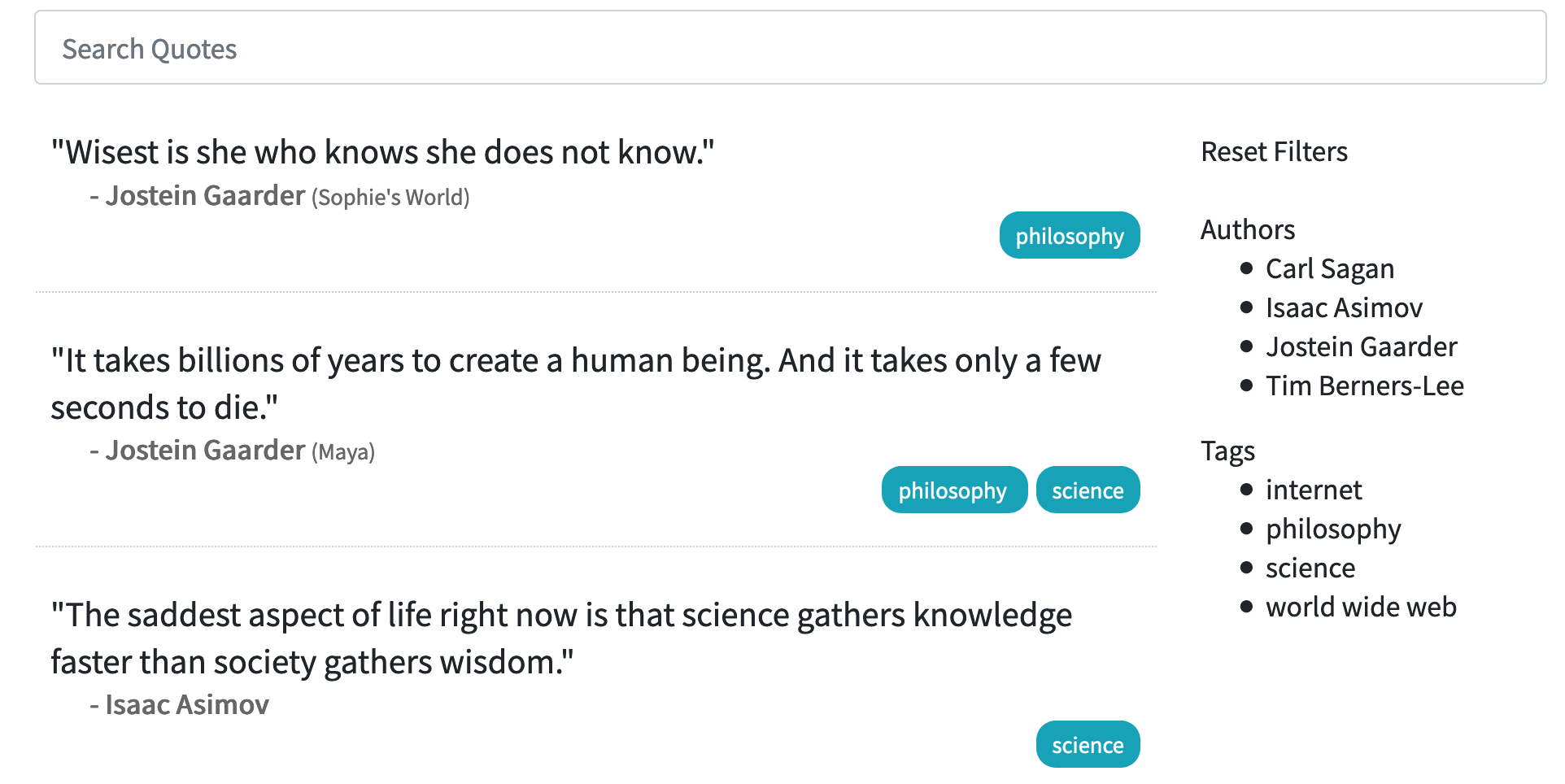
A Web App for Browsing and Searching Quotes
In this small project, I developed a Web app for browsing and search quotes that are stored on a Google Spreadsheet.
For simplicity, this app does not allow modifying the data in the spreadsheet via the Web UI. Data has to be manipulated on the Google Sheets directly. However, this allows us to skip using the Google Sheets API in this project.
Google Spreadsheet for Data Storage
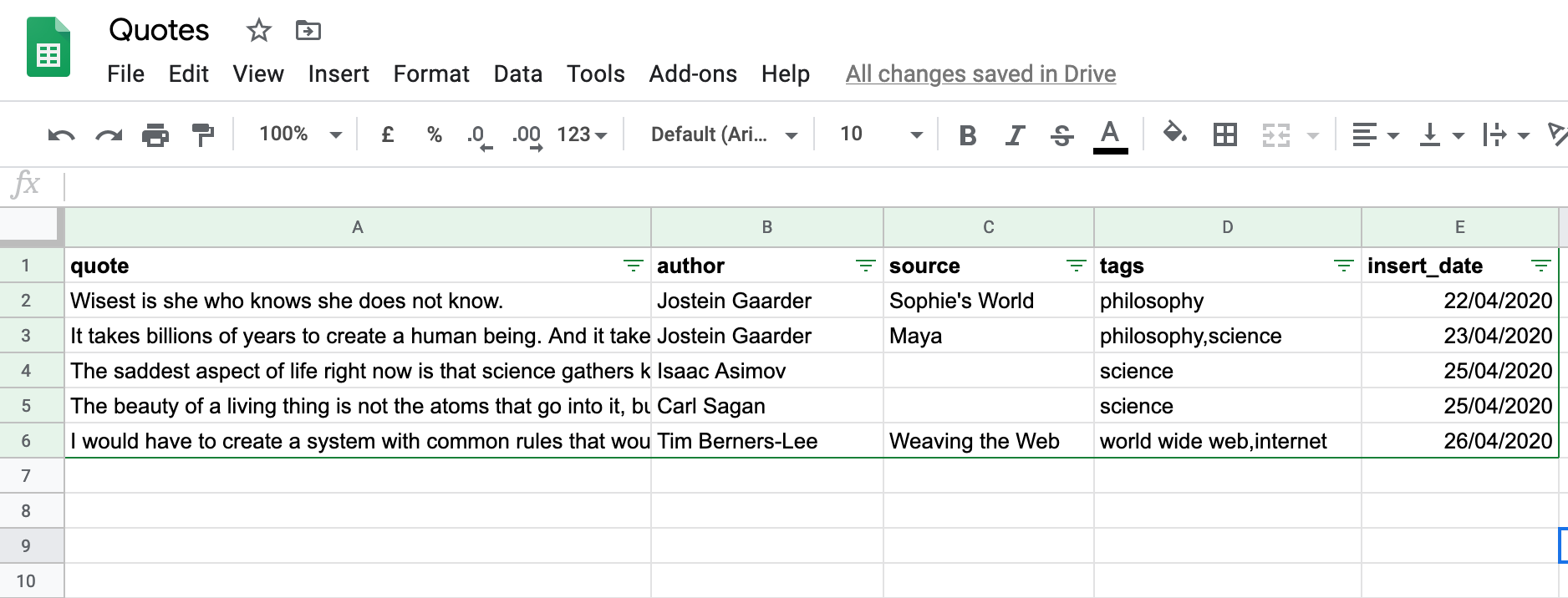
A google spreadsheet has been created to store the data, which can be found here. For the purpose of my project, I have a table with the following columns:
quote: the quotationauthor: the person who wrote or said the textsource: the source of the quotation, e.g. the name of a booktags: tags separated by commasinsert_date: date on which the quotation was inserted into this sheet (pressctrl+;on Windows orCmd+;on MacOS to quickly insert the date of today in a Google spreadsheet)
In order for the spreadsheet’s data to be avaible to other apps without the need to perform authentication, we need to first publish it. This can be done by choosing Publish to the Web from the File menu in Google Sheets.
To access the data stored in the spreadsheet, we can send a HTTP GET request to the following URL:
https://spreadsheets.google.com/feeds/list/{sheet_id}/1/public/values?alt=json
You will have to replace {sheet_id} with the ID of the Google spreadsheet in which data is stored.
Sending a request to the above URL will result in a JSON response in the following format:
{
"version": "1.0",
"encoding": "UTF-8",
"feed": {
"xmlns": "http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom",
...
"title": {
"type": "text",
"$t": "Sheet1"
},
"link": [...],
...
"entry": [
{
"id": {
...
},
...
"gsx$quote": {
"$t": "Wisest is she who knows she does not know."
},
"gsx$author": {
"$t": "Jostein Gaarder"
},
"gsx$source": {
"$t": "Sophie's World"
},
"gsx$tags": {
"$t": "philosophy"
},
"gsx$insertdate": {
"$t": "22/04/2020"
}
},
...
]
}
}
We can see that the data can be found under data.feed.entry. Values in each cell of different columns can be retrieved by using a key in the format of gsx${column_name}, such as gsx$quote.
Vue.js for Frontend Development
Vue.js is a JavaScript framework for building Web-based user interfaces and applications. In this project, it was used to develop the Web page that displays the quotations stored in the Google Sheet.
Firstly, follow the Vue.js official guide to include the necessary JavaScript file in the HTML source code:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue"></script>
In the Web page, we have an element representing the whole application:
<div id="app">
</div>
The following script is that used to load the content from the Google Sheet once the page is loaded:
var gsheet_url = "{{url_to_the_google_sheet_json}}"
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data () {
return {
info: null
}
},
mounted () {
axios
.get(gsheet_url)
.then(response => (
parseData(response.data.feed.entry)
))
}
});
The parseData function will take the list of entries in the JSON data, and store the quotations in a local data structure for display:
// Variables to hold the parsed data
var quoteList = [];
var authorList = [];
var tagList = [];
function parseData(entries) {
var authorSet = new Set();
var tagSet = new Set();
entries.forEach(function(value) {
var entry = {
"quote": value.gsx$quote.$t,
"author": value.gsx$author.$t,
"source": value.gsx$source.$t,
"tags": value.gsx$tags.$t.split(",")
};
// Add to the set of authors
authorSet.add(entry.author);
// Add to the set of tags
entry.tags.forEach(function(t) {
tagSet.add(t);
});
// Push entry into the list of quotes
quoteList.push(entry);
});
authorList = Array.from(authorSet);
authorList.sort();
tagList = Array.from(tagSet);
tagList.sort();
}
Finally, we can display the data using the template syntax provided by Vue.js. For example, the list of quotations are displayed using the following template:
<div id="quotes">
<div v-for="quote in quotes" class="quote">
<div class="quote-text">"{{ quote.quote }}"</div>
<div>
<span class="author">- {{ quote.author}}</span>
<span class="source" v-if="quote.source != ''">({{ quote.source }})</span>
</div>
<div class="tag-container">
<span v-for="tag in quote.tags" class="tag">
{{ tag }}
</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
var quotes = new Vue({
el: '#quotes',
data: {
quotes: quoteList
}
});
In this project, I also tried to implement some simple filters on the Web app to allow user to quickly filter quotations by the author names or the tags assigned to them. For details, you can refer to the source code on github.
Overall, I found this combination very useful when we want to quickly build a user interface for browsing structured data stored in a spreadsheet. This avoids the need to create a database and a backend application. I can see a lot of potentials in using this method to quickly create simple and interesting applications.